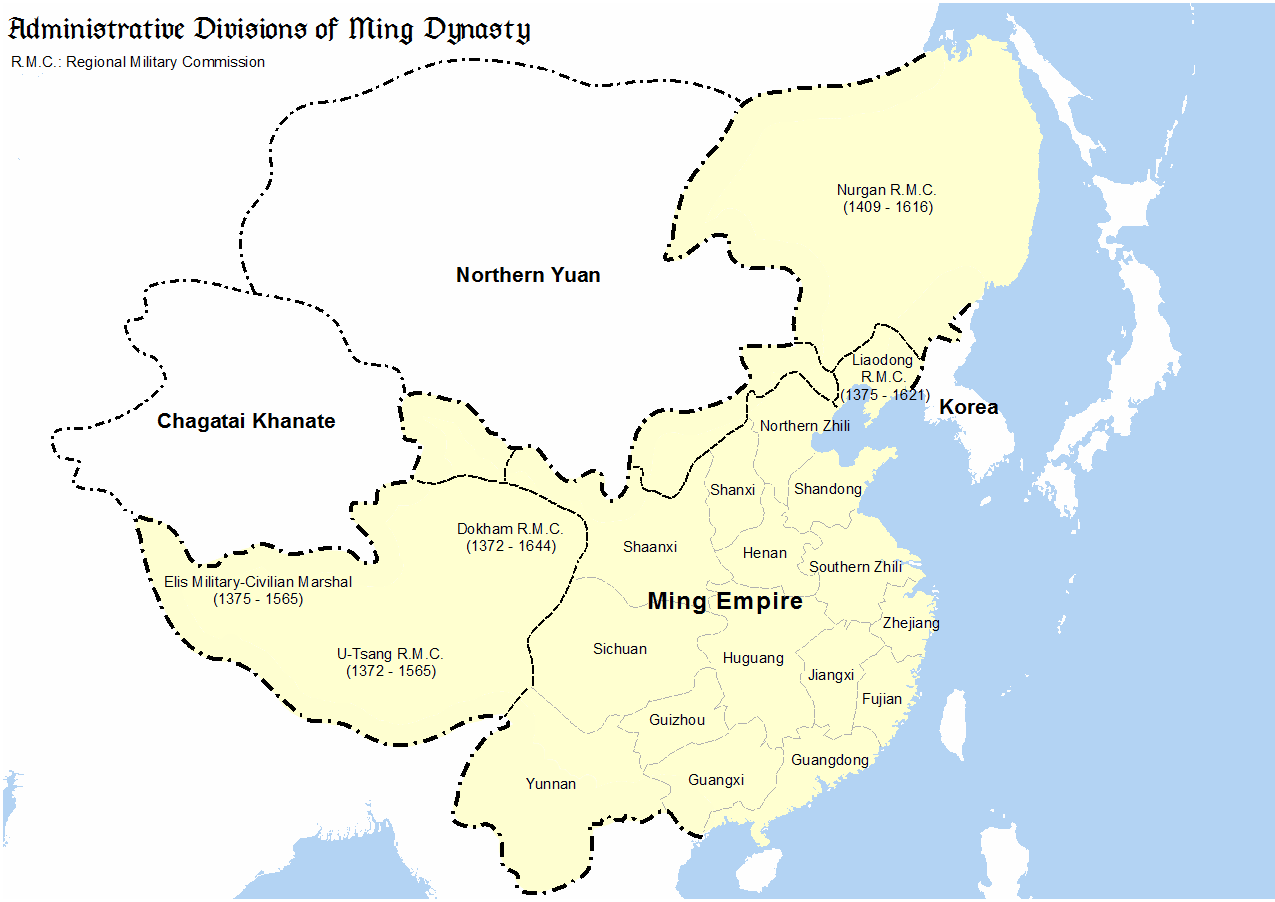
Im Jahr 1368 n. Chr. wurde die Ming-Dynastie gegründet und im selben Jahr es eroberte die Hauptstadt der mongolischen Yuan-Dynastie (das heutige Peking).
Im Jahr 1369 n. Chr. verwies der Gründungskaiser der Ming auf die Herrschaft der Yuan über Tibet: entsandte Beamte in die tibetische Region, um dort weiterhin zu regieren.
Im Jahr 1370 n. Chr. vernichteten die Ming die mongolische Armee im Nordwesten im Wesentlichen.
Im Jahr 1372 n. Chr. wurde der Ming eroberte Karakorum, die Hauptstadt des Mongolenreiches (in der heutigen Mongolei gelegen), massakrierte seine Bewohner und brannte die Stadt nieder. Bis heute ist die ehemalige Hauptstadt des Mongolenreichs eine öde Einöde.
Im Jahr 1382 n. Chr. wurde die Ming eroberte Yunnanbeseitigte das mongolische Fürstenregime, und begann mit der umfassenden Kolonisierung.
Im Jahr 1387 n. Chr., ter Ming eroberte die Mandschurei, Sieg über die in der Region stationierte mongolische Armee. Von da an unterwarf sich die Mandschurei den Ming, aUnd selbst der Gründer der Qing war ein Mandschu-Soldat, der in der chinesischen Armee diente.
Im Jahr 1388 n. Chr.**,tHe Ming fügte der Yuan-Armee, die in die mongolische Steppe in der Baikalseeregion (heute Russland) geflohen war, eine schwere Niederlage zu.** (Danach konnten die Mongolen das Land nicht mehr vereinen und gerieten in eine lange Zeit der Teilung).
Im Jahr 1407 n. Chr. Die Ming eroberten/eroberten Vietnam zurück (eine Region, die nach der Tang-Dynastie jahrhundertelang außerhalb der chinesischen Herrschaft gelegen hatte).
Die einzige Region mit anhaltenden Streitigkeiten ist Tibet, aber aktuelle Forschungen und historische Aufzeichnungen deuten darauf hin, dass die Beziehung zwischen den Ming und Tibet in der frühen Ming-Zeit keine einfache Nebenflussbeziehung war. Sogar die Qing-Kaiser erklärten, dass sie die Herrschaft der Ming übernehmen und Tibet regieren würden. Nach dem Niedergang der Ming-Dynastie manifestierte sich die Beziehung zwischen Tibet und der Ming-Dynastie hauptsächlich als Tributbeziehung.
Nian’er, die westlichen Regionen haben den Buddhismus immer respektiert und China gedient, das bereits etabliert ist. Wenn das kaiserliche Edikt und der Siegelbrief der Ming-Dynastie vorgezogen werden, werde ich es ändern und gewähren, genau wie in der alten Praxis. „Der Qing-Kaiser sagte, sie würden die Herrschaft der Ming-Dynastie übernehmen und Tibet regieren.
Streng genommen waren die von den Mandschu gegründeten Qing-Dynastien und die von den Mongolen gegründeten Yuan Dynastien, die von Eindringlingen gegründet wurden. Natürlich basierten ihre Regime hauptsächlich auf chinesischem Territorium. Obwohl das moderne China nominell ein multiethnisches Land ist und über eine große Zahl von Mongolen und fast alle Mandschu herrscht, waren die Mandschu im damaligen Kontext zweifellos Eindringlinge. (Die Ming definierten die Mandschus offiziell als minderwertige Barbaren, und während der Xinhai-Revolution 1911 lautete der Slogan der Republik China "Vertreibe die Barbaren und stelle China wieder her," sogar ein groß angelegtes Vergeltungsmassaker gegen die Mandschu.
Von Wise-Pineapple-4190
10 Kommentare
Mao Zedong (founder of the ROC) once described the Ming Dynasty as perhaps one of the most corrupt dynasties in Chinese history.
Indeed, the Ming’s ultimate demise was due to its corruption, leading to the collapse of its entire financial and military system. In 1644, the Ming was destroyed by a large-scale internal uprising in China.
However, the Ming also holds great significance for the Chinese .
The Mongol Yuan and Manchu Qing dynasties ruled China for 360 years. Without the Ming , China would have been under foreign rule for over 600 years.
In such a situation, national identity and cultural continuity would have faced enormous problems.
Therefore, even today, the Ming is still beloved by many Chinese.
In 1911, after destroying Manchu rule, the founder of the ROC immediately went to Nanjing to pay homage to the Ming emperor. His eulogy read: „The great emperor of the past destroyed the rule of barbarians and founded the great Ming Dynasty. However, his descendants were unfilial; 270 years later, the barbaric Manchus took advantage of China’s severe internal strife to invade and rule China.“
Today, in the name of restoring China and destroying Manchu rule, I lead all civil and military officials to pay homage to the great Ming Dynasty emperor.
Haha, it seems many Westerners are still more familiar with the Mongols. I posted maps of the Han and Tang dynasties, but they didn’t get many likes because most people aren’t familiar with them.
Although most people don’t know about the Ming dynasty either, as the Chinese dynasty that destroyed Mongol rule and repeatedly invaded the Mongolian steppes, it immediately attracted the attention of many Europeans and Americans, and the number of likes exceeded 10 in just a few minutes.
When the Manchus invaded Korea and demanded that we sever ties with the Ming dynasty, defeat was almost inevitable, and even surrender would not have meant particularly harsh terms.
Yet Korea could not submit, because several decades earlier, when Japan invaded Korea, the Ming dynasty had come to our aid despite the immense burden it placed on itself.
The Ming dynasty is probably the dynasty that is viewed most positively in Chinese history, not only by the Chinese, but also by Koreans.
What does RMC mean?
The Last Dynasty, the Communist Party
I always found it interesting how even during the height of the age of exploration the Ming never seriously engaged in colonialism. Even in places with greater Chinese influence like Indonesia, or Malaysia.
Tibet was in no way a part or under the Ming. Nor did the Ming ever rule Tibet.
Go ahead and cite this “current research and historical records”
What OP is trying to talk about is the history of the Han Chinese, not the history of China.
In actual Chinese history, foreigners conquered and unified China and ruled it for thousands of years, and even up until a hundred years ago, most of Han Chinese people were peasants or slaves.
Major Foreign Dynasties in China.
Northern Wei Dynasty (北魏): Established by the Xianbei. Period: 386 CE – 534 CE.
Liao Dynasty (遼): Established by the Khitan. Period: 916 CE – 1125 CE.
Jin Dynasty (金): Established by the Jurchen. Period: 1115 CE – 1234 CE.
Yuan Dynasty (元): Established by the Mongol. Period: 1271 CE – 1368 CE.
Qing Dynasty (淸): Established by the Manchu. Period: 1644 CE – 1912 CE.
This is the real Ming with its tribute states.
[https://www.reddit.com/r/MapPorn/s/RSGViDKgLC](https://www.reddit.com/r/MapPorn/s/RSGViDKgLC)
While technically true.. the Manchu rulers by the 1800s have adopted a lot of Chinese culture.
You could say the British Monarchy havent been British in a long time either. The „Windsor“ dynasty is more Germanic than your typical British-Anglo/Saxon/Norman ancestry. They renamed their dynasty and adopted British names to appeal to the British public.