Die Han-Dynastie: Eine Dynastie, die die nationale Identität Chinas endgültig begründete.
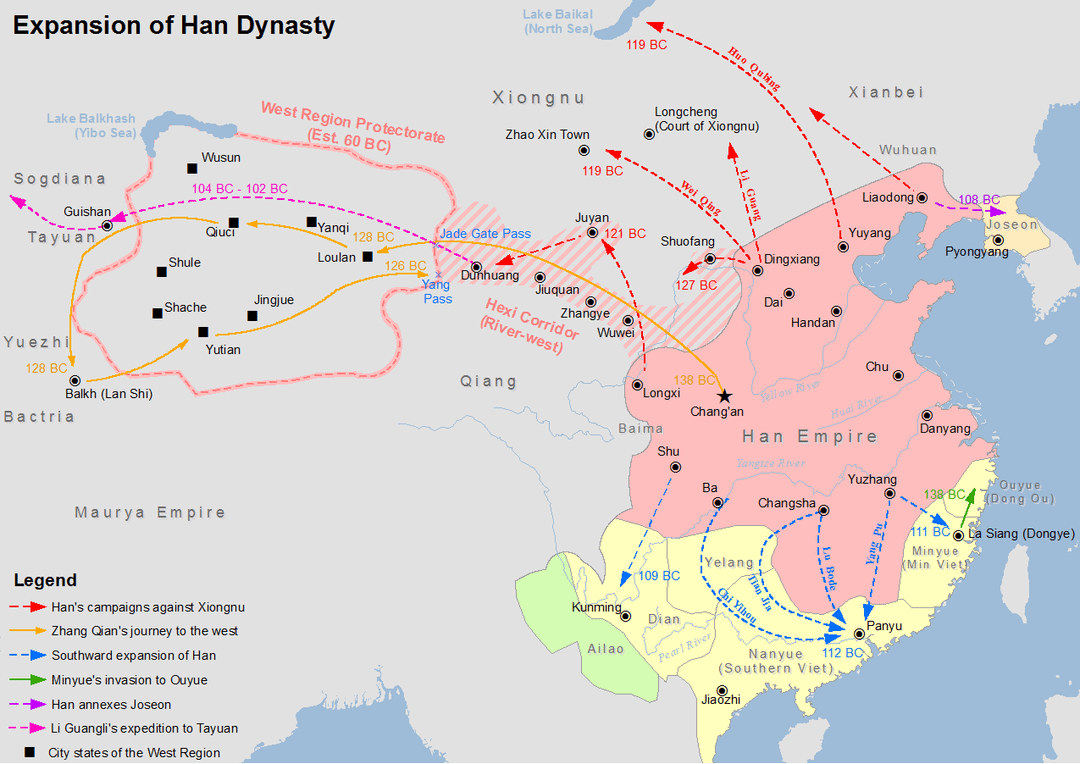
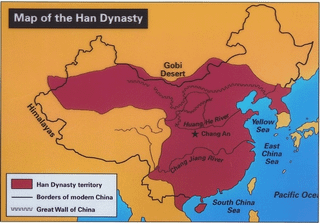
Es überlebte etwa 400 Jahre und umfasste zunächst nur 2 bis 2,5 Millionen Quadratkilometer, dann wuchs es auf eine Spitzengröße von 6 bis 6,5 Millionen Quadratkilometern an.
Es eroberte und annektierte bis heute die südchinesischen Provinzen (Guangxi, Guangdong und Fujian); eroberte und annektierte Vietnam; eroberte Nordkorea; besiegte und vertrieb das Nomadenreich Xiongnu; annektierte den Hexi-Korridor (Teile der heutigen nordchinesischen Provinzen) und Teile der Inneren Mongolei; und nach dem Sieg über den zentralasiatischen Staat Dayuan annektierte es Teile von Xinjiang in Zentralasien.
Von Wise-Pineapple-4190
2 Kommentare
[removed]
Although the Qin Dynasty unified China for the first time, its existence was short-lived, lasting only a little over a decade. The Han Dynasty, however, greatly expanded China’s territory and lasted for over 400 years, defeating virtually every enemy it could in its surrounding regions.
The most famous Xiongnu people, according to modern genetic testing, are ancestors of many European Hun people. After being ultimately defeated by the Han Dynasty in the 1st century AD, some were forced to migrate to other regions.
From then on, the Han Dynasty endowed the Chinese people with a stable and unified national identity.
From then on, poets and officials of Chinese dynasties such as the Tang, Song, and Ming preferred to refer to themselves as Han, a fact clearly evident in numerous poems and official records.
The Ming Dynasty and the ROC, which destroyed Mongol and Manchu rule, also advocated restoring Han rule and expelling the „barbarians.“
Therefore, even today, the Han Dynasty is still considered by most Chinese people to be the greatest Chinese dynasty.